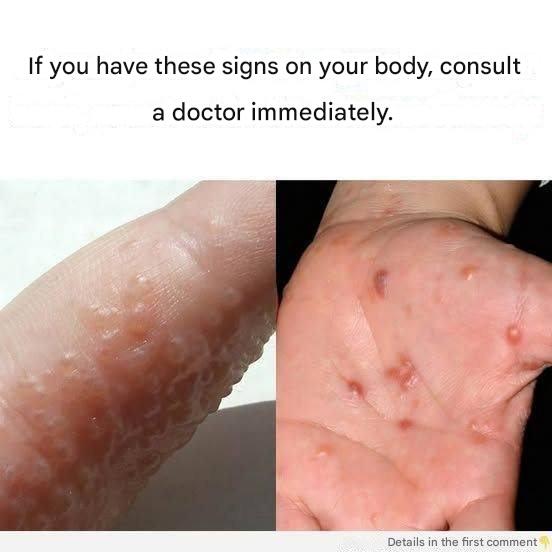
Physical examination: A doctor will examine the affected areas, paying particular attention to blisters and the surrounding skin.
History of the patient: Your doctor may ask you about your activities, including if you are working with metals or if you have been exposed to new products.
Allergy test: To determine if your eczema is triggered by allergens, such as nickel or cobalt, the doctor may perform an allergy test.
Skin sample: In some cases, a small skin sample may be taken to test infections or other underlying conditions that could contribute to the outbreaks.
Early diagnosis can help to manage symptoms more effectively and prevent complications.
Home remedies against light thrust
For mild cases of dyshydroic eczema, home remedies can often help relieve symptoms and speed up recovery. Here are some strategies:
Cold compresses: Applying a cold compress to the affected area two to four times a day for 15 minutes may help to reduce itching and inflammation.
Hydrate: Use a thick, fragrance-free moisturiser or barrier restorative cream immediately after a bath or compress to retain moisture.
Corticosteroid creams: Over-the-counter corticosteroid creams can help reduce inflammation and cure blisters more quickly.
Anti-itching medicines: Anti-itching creams or oral antihistamines may relieve persistent itching.
Stress management: Techniques like meditation, deep breathing or yoga can help reduce stress, a common trigger for eczema flare-ups.
Carey for avoiding potential irritants, such as aggressive soaps or allergens, may prevent the symptoms from getting worse.
Dietary changes to manage eczema
Nickel and cobalt, which are common triggers of dyshydrootic eczema, are present in various foods. If your doctor suspects an allergy to nickel or cobalt, he may recommend that you change your diet. However, since foods containing these elements are often rich in nutrients, it is essential to work with a healthcare professional before making radical changes.
Some common foods that contain nickel include:
Cereals
Soybean products
Legumes
Chocolate and cocoa
Dry fruit
Cobalt, on the other hand, is found mainly in foods rich in vitamin B12, including dairy products, meat and poultry.
A point-based diet may be needed to limit your exposure to these allergens, but always seek professional advice before implementing dietary restrictions.
Medical treatment of severe dyshydrosis eczema
If home remedies do not relieve enough or if flare-ups become severe or frequent, medical treatment may be necessary. Common treatments include:
Prescription steroid creams: they are more powerful than over-the-counter options and can rapidly reduce inflammation.
Topical medicines: Medicines such as pimecrolimus cream or tacrolimus ointment may suppress the immune response that leads to eczema.
Systemic medicines: In cases where topical treatments do not work, oral or injectable medicines may be prescribed to suppress the immune system.
Luminotherapy: Also known as phototherapy, this treatment uses controlled exposure to UV light to reduce symptoms.
Stress management techniques: The management of stress through therapy or biofeedback can help to mitigate stress-related relapses.
In severe cases, doctors may recommend a combination of treatments to control symptoms.
Complications of dyshydromatic eczema
Although dyshidrotic eczema does not put life at risk, it can significantly affect quality of life. Here are some common complications:
Difficulty in performing daily tasks: Walking, working or even using your hands can become difficult during relapses.
Infection: Scratching blisters may cause open wounds, increasing the risk of skin infections. If the area becomes red, swollen or painful, seek medical advice immediately.
Sleep disorder: Itching and discomfort can make sleep difficult, affecting your general well-being.
Early and effective management of symptoms can help prevent these complications.
Preventing outbreaks of dyshydroic eczema
The following page continuation