From digestive disorders to skin problems, including chronic fatigue and autoimmune diseases, gluten sensitivity can manifest discreetly but significantly. Recognizing these signals is essential to avoid complications and improve your quality of life. What are these signs, and how do we respond effectively?
The Ten Signs to Watch Closely
Persistent digestive disorders
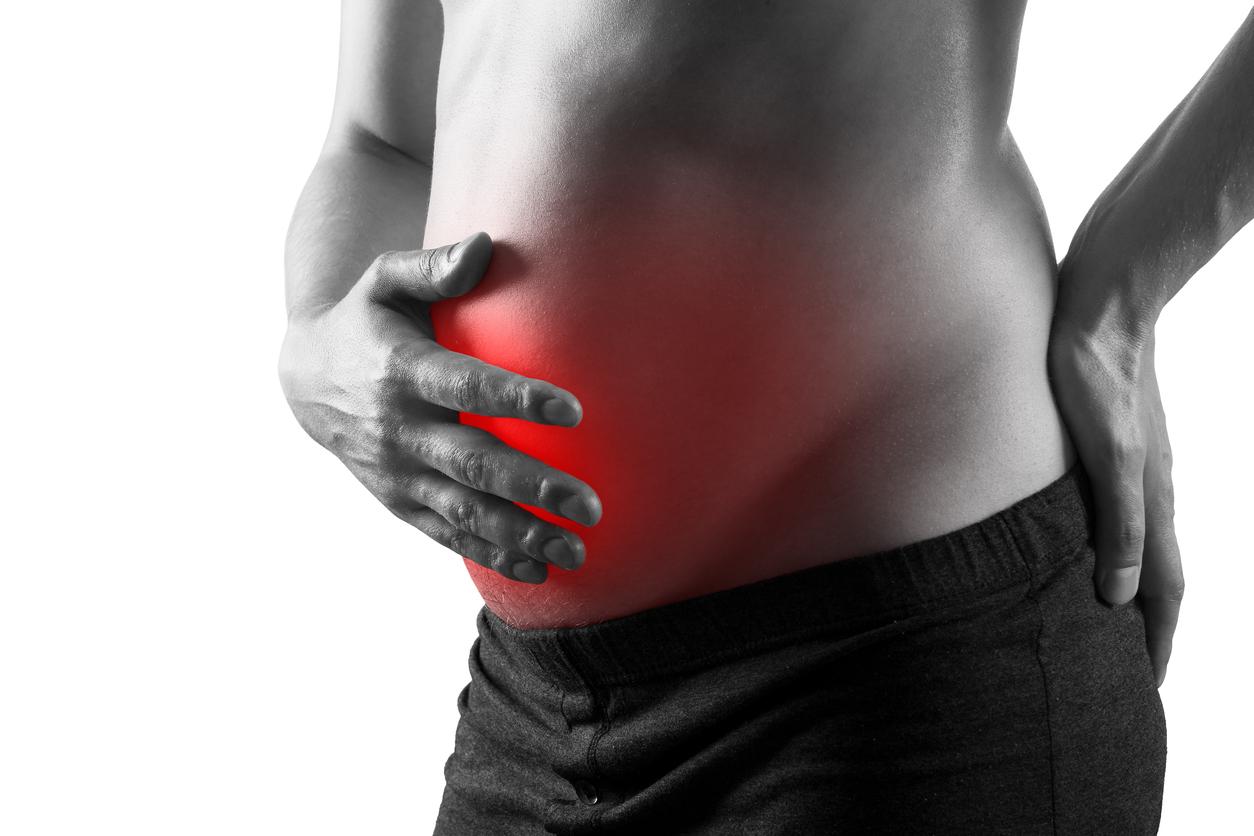
Blowing, nausea, diarrhoea or chronic constipation are symptoms often associated with gluten tenderness. These disorders are commonly confused with irritable bowel syndrome, which is a delaying syndrome and an accurate diagnosis. If these symptoms persist despite a balanced diet, it may be useful to take a test to assess your sensitivity to gluten.
Unexplained weight fluctuations
Sudden and no apparent reason intake or weight loss may be a sign of inflammation related to gluten intolerance. This reaction disrupts metabolism, causing nutritional deficiencies and unexpected weight variations.
Hormonal imbalances
Gluten can affect hormones, cause irregular menstrual cycles, exacerbated premenstrual syndrome or sleep disorders. These disturbances are particularly common during key hormonal periods such as puberty, pregnancy or menopause, especially in women.
Brain fog and nervous disorders

Difficulty in concentrating, chronic fatigue, irritability or frequent migraines may be related to inflammation due to gluten. Migraines, in particular, often appear 30 to 60 minutes after the consumption of products containing gluten.
Skin problems and frailty of the nails
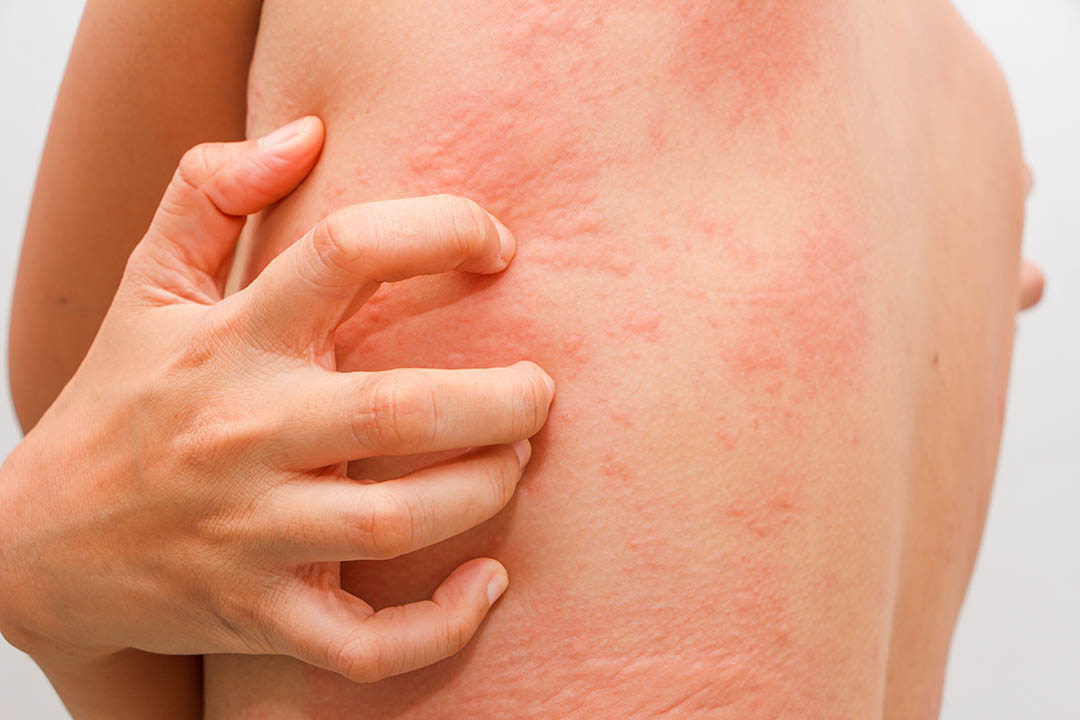
Gluten intolerance can result in skin conditions such as dermatitis herpetiforms or eczema, often accompanied by itching and irritation. In addition, your nails can become brittle and fragile, as a result of nutritional deficiencies linked to this sensitivity.
Hyperactivity and disturbance of attention
In both children and adults, ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) may be aggravated by gluten. Adopting a gluten-free diet could help reduce symptoms such as agitation and difficulty concentrating.
Poor oral health
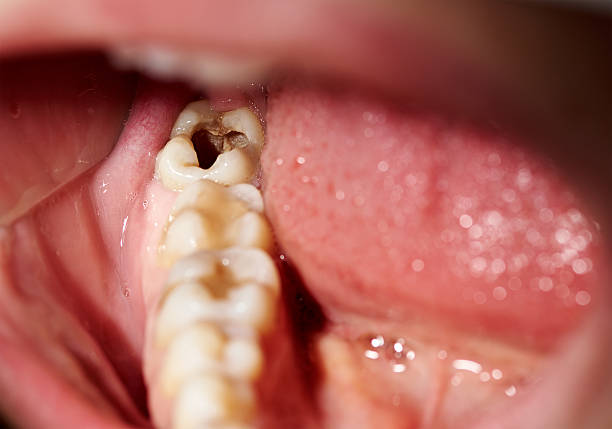
Hypersensitivity of enamel, frequent caries or recurrent mouth ulcers may be a sign of calcium malabsorption caused by gluten intolerance. If these oral-dental problems persist despite impeccable hygiene, it may be useful to consult a specialist.
Fatigue and iron deficiency anaemia
Iron deficiency is a common symptom of celiac disease, manifested by chronic tiredness, shortness of breath or pale skin. This leads to poor absorption of iron in a intestine damaged by gluten.
read on the next page
