What to do if you find a swollen bump or ganglion on your neck, back or ear
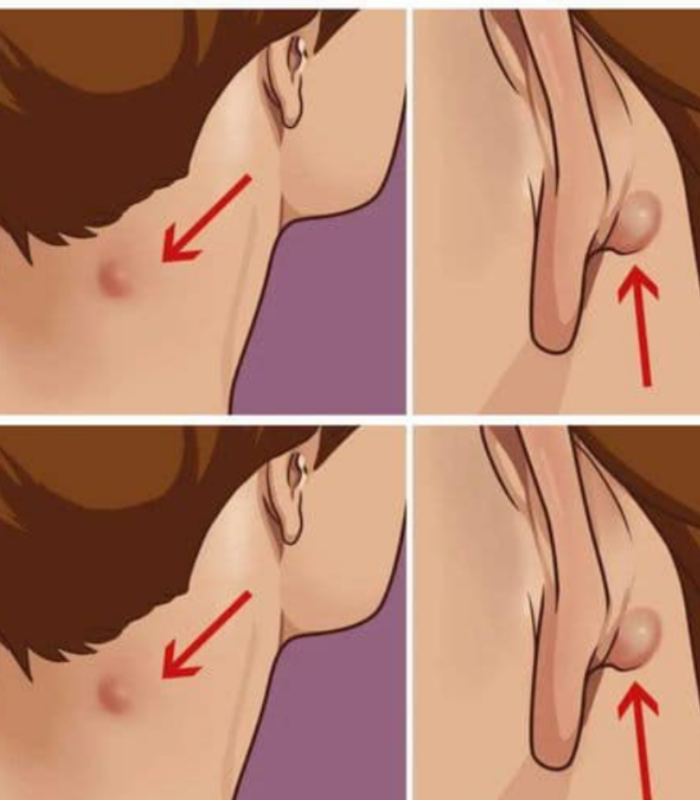
The most common cause of swelling of the lymph nodes is infection. When the body fights bacteria or viruses, the activity of the lymph nodes increases, causing them to widen. Common infections include:
- Upper respiratory tract infections: Diseases such as colds, flu or tonsillitis often cause swelling of the neck lymph nodes.
- Ear infections: Middle ear infections may cause swelling of the glands near the ear.
- Dental infections: Abscesses or other inflammations of the oral cavity may cause enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes.
In addition to infections, other factors may also cause enlarged lymph nodes:
- Autoimmune diseases: Diseases such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can cause chronic swelling of the glands.
- Tumour diseases: In some cases, hypertrophic lymph nodes may be associated with lymphomas or metastases from other tumours.
Although the enlarged lymph nodes are often benign and temporary, there are situations where it is appropriate to consult a doctor about this condition:
- The lymph nodes remain enlarged for more than two to three weeks.
- The bumps are hard, motionless or develop rapidly.
- Presence of concomitant symptoms such as fever, night sweats, unexplained weight loss or tiredness.
- History of cancer or weakened immune system.
In case of persistent swelling of the glands, your doctor will usually perform a physical examination and may recommend additional tests, such as blood tests, ultrasounds or biopsies, to determine the cause of the problem.

Treatment depends on the underlying cause:
Continue reading the article on the next page.